Navigating India's Conduct Discipline and Appeal Rules
- Rare Labs
- Oct 19, 2025
- 16 min read
When you're working in the government or public sector in India, you'll often come across something called "Conduct, Discipline, and Appeal" rules, or CDA rules. Think of this as the official playbook for professional behaviour.
It's a structured framework that lays out what's expected of an employee, what happens if someone steps out of line, and how they can challenge any disciplinary action. The whole point is to keep things fair, balancing the organisation's need for integrity with an individual's rights.
Unpacking the Framework for Workplace Justice

Navigating employment regulations can feel like you've been handed a complex rulebook with no guide. The CDA rules are that essential guide. They are built on three core pillars, and understanding them is crucial for both employees and management to maintain a fair and professional workplace.
Let's break them down.
Defining Professional Misconduct
First up, what exactly is ‘misconduct’ in a professional setting? It’s a much broader term than just "breaking the law." Misconduct is any action that violates the organisation's established code of conduct.
This could be anything from habitual lateness and refusing to follow instructions to more serious issues like financial fiddling or harassment. At its heart, misconduct is any behaviour that could damage the reputation, efficiency, or integrity of the organisation. These rules draw a clear line in the sand.
InsightsMisconduct isn't just about what you do, but also what you don't do. Negligence or a serious dereliction of duty, like failing to follow mandatory safety protocols, can also be classified as misconduct, even if there was no malicious intent.
The Purpose of Disciplinary Action
When misconduct is suspected, a disciplinary process kicks off. A lot of people see this as purely a way to punish someone, but that's a misconception. It’s better to view it as a corrective system.
The goal isn't just to hand out penalties. It’s about fairly investigating the allegations, upholding workplace standards, and discouraging similar behaviour in the future. The entire process is meant to be governed by the principles of natural justice, ensuring that decisions aren't made on a whim.
The Fundamental Right to Appeal
This brings us to the appeal process, which is arguably the most important safety net for an employee's rights. It gives you a formal way to challenge a disciplinary decision if you feel it was unfair, too harsh, or that the proper procedure wasn't followed.
This right to appeal creates a system of checks and balances. It’s there to prevent a potential miscarriage of justice.
This is an area where legal AI tools are becoming incredibly helpful. For example, a tool like Draft Bot Pro can help you dissect a disciplinary order and structure a solid appeal. It can guide you in articulating your points clearly and referencing the right service rules, which can level the playing field when you're presenting your case to the higher authority.
The Core Principles of a Fair Disciplinary Process
Every set of conduct, discipline, and appeal rules is built on one simple idea: fairness. This isn't just a feel-good concept; it's a solid legal principle known as 'natural justice'. Think of it as the impartial referee in a high-stakes match, making sure both sides play by the same rules.
Natural justice itself stands on two unshakable pillars. If either of them crumbles, any disciplinary action taken becomes shaky and can easily be challenged and overturned. Getting a handle on these principles is your first step to confidently navigating any workplace inquiry.
The Right to Be Heard
The first pillar comes from a Latin maxim: _Audi Alteram Partem_, which simply means "hear the other side." This is the single most fundamental right you have in any disciplinary process. It means no decision can be made against you until you’ve had a fair chance to present your side of the story.
But this isn't just about letting you have your say. It breaks down into a few critical rights:
Clear Notice: You must be told, in writing, exactly what you're being accused of. Vague allegations just don't cut it.
Sufficient Time: You have to be given a reasonable amount of time to get your defence ready.
Opportunity to Rebut: You have the right to see all the evidence being used against you and to challenge it, which includes cross-examining any witnesses.
At its heart, this principle stops one-sided decisions based on incomplete information. It forces the decision-maker to get the full picture before making a call.
The Rule Against Bias
The second pillar is just as crucial: _Nemo Judex in Causa Sua_, meaning "no one should be a judge in their own cause." This principle gets straight to the problem of bias. The person or committee deciding your case must be completely impartial, with no personal stake in how it turns out.
Imagine a cricket umpire who is also the captain of one of the teams. Would you trust their decisions? Of course not. The same logic applies here. The disciplinary authority has to be neutral, without any prejudice or conflict of interest that could sway their judgment. This ensures the final decision is based purely on the facts and evidence.
This infographic really brings home how these two pillars work together to create a balanced, fair system.
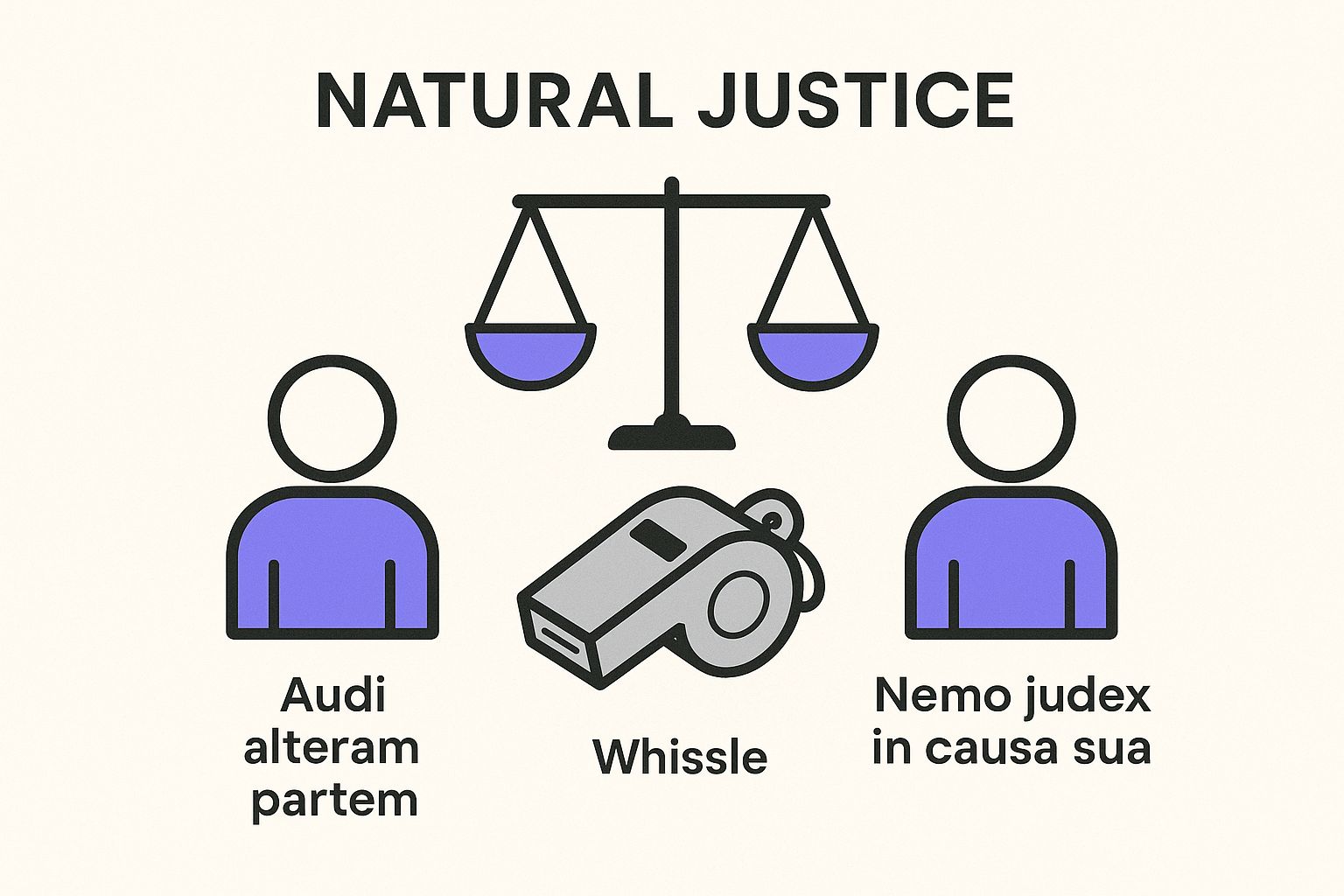
Just like a good referee, impartiality and the right to be heard are the cornerstones holding up the entire structure of a just disciplinary process.
Navigating the Inquiry Process
These principles aren't just legal theory; they are hardwired into the step-by-step procedure of any departmental inquiry. From the first notice to the final order, every stage is designed to uphold fairness and ensure no steps are skipped.
This structured approach has deep roots in Indian law. The Conduct, Discipline and Appeal (CDA) Rules are specifically designed to guarantee fair treatment and accountability. A great example is the All India Services (Discipline and Appeal) Rules, 1969, which provides a detailed playbook for top civil servants, covering everything from potential penalties to appeal timelines. The rules even specify that appeals must be filed within one month, showing a systematic government approach that has been in place for over fifty years. You can explore the foundational rules for All India Services to see these principles in action.
InsightsA very common mistake that can get an entire inquiry thrown out is a defective charge sheet. If the charges are vague, lump multiple different allegations into one, or don't list the documents being relied upon, the whole case is built on sand. This is often a powerful ground for appeal.
This is where modern tools can make a huge difference. A legal AI assistant like Draft Bot Pro can act as your procedural checklist. For an employee, it can help you write a detailed, point-by-point reply to a show-cause notice. For an employer, it helps generate compliant notices and charge sheets, drastically cutting the risk of procedural errors that could derail the entire disciplinary action. By keeping both sides on the right track, it helps uphold the principles of natural justice for everyone involved.
Understanding Disciplinary Actions and Penalties
So, what happens when someone breaks the organisation's code of conduct? The process isn't just a slap on the wrist; it moves towards a specific, calculated outcome—the penalty. Under the official conduct, discipline, and appeal (CDA) rules, penalties aren't pulled out of a hat. They are carefully categorised to make sure the punishment fits the crime. This idea of proportionality is the bedrock of the entire system.
Think of it like a referee in a football match. A minor foul might just earn a yellow card—a stern warning. But a reckless, dangerous tackle? That’s an immediate red card, sending the player off the field. Workplace disciplinary actions work on a similar logic, splitting penalties into two clear camps: minor and major.
Minor Penalties: A Minor Setback
Minor penalties are really corrective nudges. They're designed to send a clear message that a certain behaviour needs to change, but without derailing an employee's entire career. It's the system’s way of saying, “We're not happy with this, but you can bounce back.”
Some common minor penalties you might see are:
Censure: This is a formal, written scolding that gets officially placed on your record. It’s a serious mark of disapproval.
Withholding of Promotion: If you were in line for a promotion, it could be put on hold for a specific period.
Recovery of Loss: Did your mistake cost the organisation money? They might recover that amount directly from your salary.
Withholding of Increments: This means your next scheduled pay raise is paused for a set time, though it usually doesn't affect future raises down the line.
These penalties sting, no doubt, but they are designed as setbacks you can recover from.
Major Penalties: A Career-Altering Impact
Major penalties are a different beast altogether. These carry severe, often permanent, consequences for an employee’s career and livelihood. They are reserved for serious misconduct where a simple course correction just won't cut it.
The fallout from a major penalty is profound. We're talking about actions like:
Reduction to a Lower Rank or Grade: A straight-up demotion. This hits your status, your pay, and your responsibilities hard, and can be a massive blow to your career momentum.
Compulsory Retirement: You’re forced to retire early, though you usually get to keep your retirement benefits.
Removal from Service: Your employment is terminated, but the door isn't completely shut—you aren't technically disqualified from future government jobs.
Dismissal from Service: This is the ultimate penalty. It's not just termination; it’s a permanent black mark that disqualifies you from any future government or public sector employment.
Because the stakes are so incredibly high, the procedure for handing out a major penalty is far more strict and detailed than for a minor one. It always requires a full-blown formal inquiry.
To help clarify the differences, let's break it down.
Minor vs Major Penalties Under CDA Rules
Penalty Type | Examples | Typical Procedure Required |
|---|---|---|
Minor | Censure, Withholding of Promotion, Recovery of Pecuniary Loss, Withholding of Increments | Usually, a Show Cause Notice is issued, and the employee provides a written explanation. A formal inquiry is not mandatory. |
Major | Reduction in Rank, Compulsory Retirement, Removal from Service, Dismissal from Service | Requires a full, formal departmental inquiry. This includes framing a charge sheet, appointing an Inquiry Officer, presenting evidence, and allowing the employee to cross-examine witnesses. |
Understanding which category a potential penalty falls into is crucial because it dictates the entire defence strategy.
InsightsHere’s a critical point many people miss: the standard of proof in these departmental inquiries isn't the same as in a criminal court. A criminal case needs proof "beyond a reasonable doubt." Disciplinary proceedings, however, run on a "preponderance of probability." This simply means the disciplinary authority only has to be convinced that it's more likely than not that you committed the misconduct. This lower bar makes a strong, well-argued defence absolutely essential from day one.
Your first chance to build that defence is your reply to the charge sheet. A vague, sloppy, or emotional response can sink your case before it even begins. This is where modern tools can give you a serious edge. A legal AI tool like **Draft Bot Pro** can be a game-changer. It helps you structure a powerful, point-by-point rebuttal to every single allegation. The AI ensures you correctly cite the specific service rules relevant to your case, turning a simple denial into a well-reasoned legal argument. By helping you build a logical and procedurally sound response, it lays the strongest possible foundation for your defence, whether you're fighting a minor censure or staring down the threat of dismissal.
How to Construct a Powerful Appeal

Getting hit with an unfavourable disciplinary order can feel like the end of the road. It’s a gut punch, but it’s not the final word. The appeal process is a fundamental right woven into the conduct discipline and appeal rules, giving you a critical second chance to make your case.
Building a winning appeal isn’t about venting frustration. It’s about precision. You need to become a surgeon, methodically dissecting the original decision to build a rock-solid, logical argument for why it should be overturned or changed.
Think of the inquiry report and final order like a faulty engine. Your first job is to pop the hood and find exactly what went wrong. A successful appeal is built on identifying specific, undeniable weaknesses in the disciplinary authority’s case.
Dissecting the Disciplinary Order
Before you even think about writing your appeal, you have to do your homework. This means a deep, critical dive into the inquiry report and the final penalty order. You’re not just reading it; you're hunting for the cracks in its foundation.
Your review should zero in on three key areas:
Procedural Flaws: Was the rulebook followed to the letter? Were you given proper notice? A copy of the charge sheet? A real opportunity to defend yourself and cross-examine witnesses? Any misstep in the required procedure is a powerful lever for your appeal.
Factual Errors: Go over the evidence with a fine-tooth comb. Did the Inquiry Officer get the facts wrong, ignore crucial evidence you submitted, or lean on shaky testimony? A decision built on a house of cards—or incorrect information—is bound to crumble.
Disproportionate Penalty: Does the punishment fit the crime? If a minor slip-up resulted in a major penalty, you have a strong argument. The principle of proportionality is a cornerstone of fairness, and a penalty that's excessively harsh is a classic ground for an appeal.
As you build your case, remember that some situations are more complex than others. For issues tangled up with discrimination or serious procedural violations, it's wise to consider when to get an expert involved. Knowing when to hire a discrimination lawyer can be a game-changer in protecting your rights.
Structuring Your Appeal Memo
Once you’ve identified your grounds for appeal, it's time to put them on paper. Your appeal memorandum is your formal argument to the higher authority. It needs to be clear, professional, and persuasive to make a real impact.
Every strong appeal memo should include these core components:
A Clear Introduction: Start by stating who you are, which order you're appealing against, and the date it was issued. No fluff.
Grounds for Appeal: This is the heart of your document. Tackle each ground in a separate paragraph. Clearly explain the procedural mistake, the factual error, or why the penalty is disproportionate.
Supporting Evidence: Don’t just make claims—back them up. Refer to specific documents, witness statements, or pages from the inquiry report that prove your point.
The Prayer for Relief: End with a clear, direct statement of what you want. Do you want the penalty cancelled entirely? Reduced to something lesser? A whole new inquiry? Be specific.
Don't forget the clock is ticking. Timeliness is everything. Most organisations have strict deadlines for filing appeals. For instance, in public sector undertakings like Coal India Limited (CIL), the CDA Rules give you just one month from receiving the order. Miss that window, and your appeal might be thrown out without anyone even reading it.
InsightsHere’s a little secret: many of the most successful appeals don't hinge on proving total innocence. They win by pointing out fatal procedural mistakes made by the disciplinary authority. Things like denying a fair chance to be heard, relying on secret evidence, or an obviously biased Inquiry Officer can completely invalidate the entire process.
Pulling together such a structured and compelling appeal is tough work. This is where a legal AI assistant like Draft Bot Pro can be a massive help. The platform guides you in organising your arguments and structuring your appeal memo with the right logical flow. You input the case details, and the AI helps you craft clear, articulate points for each ground of appeal. This ensures your final document is not just complete but also formatted perfectly for the appellate authority. It’s also great for drafting other key documents; you might find our guide on using AI for show cause and warning letters helpful.
How CDA Rules Differ Across Indian Sectors
While the core principles of fairness are the same all over India, the specific conduct, discipline, and appeal (CDA) rules are definitely not a one-size-fits-all deal.
Think of it this way: the game is still cricket, but the pitch conditions and local ground rules change dramatically depending on where you're playing. The service rules that govern you work the same way—they depend entirely on where you're employed.
The regulations for a Central Government employee, a manager at a Public Sector Undertaking (PSU), or a state civil servant all have their own distinct flavour. Each is tailored to the unique structure and purpose of its sector, and knowing these differences is key to navigating the disciplinary process correctly.
Central Civil Services vs Public Sector Undertakings
The most well-known framework is the Central Civil Services (Classification, Control and Appeal) Rules, or the CCS Rules for short. These are the rulebooks for employees working directly for the Central Government. They are incredibly detailed, heavy on procedure, and have been shaped by decades of administrative law.
Public Sector Undertakings, on the other hand, operate more like private companies, even though they are government-owned. Their CDA rules often reflect this dual identity. For instance, PSU rules frequently bring in things like corporate governance, performance metrics, and business ethics—concepts you just won't find in the standard civil service rulebook. The disciplinary authority in a PSU might be a Board of Directors or a management committee, mirroring a corporate structure rather than a purely administrative one.
The Role of State-Specific Rules
Just to add another layer of complexity, every Indian state has its own set of rules for its employees. While they follow the same basic principles as the central rules, they're packed with regional specifics and procedural quirks.
For example, frameworks like the Tamil Nadu Civil Services (Discipline and Appeal) Rules of 1973 govern state employees with meticulous detail. These rules spell out everything from how complaint committees are formed to the exact timelines for appeals, building in multiple layers of oversight.
This structured approach shows the government's commitment to preventing arbitrary decisions and protecting employee rights. You can explore the detailed procedures within the Tamil Nadu Civil Services rules to see just how deep they go.
InsightsA common point of confusion is how these rules apply to temporary or contractual employees. Generally, temporary government servants are covered by the CCS (Temporary Service) Rules, which provide a simpler, often faster, disciplinary process.Contractual employees are a different story. They are typically governed only by the terms of their specific employment contract. This means their disciplinary procedures and appeal rights are limited to what’s written in that agreement, which can be far less protective than the standard CDA rules.
Trying to make sense of this maze of regulations can be a real headache. This is where a Legal AI like Draft Bot Pro can be a game-changer. By asking a few targeted questions about your employment sector—whether you're central, state, or PSU—it helps pinpoint the exact set of rules that apply to your situation.
This ensures that any document you create, from a reply to a charge sheet to an appeal memo, is perfectly aligned with the specific regulations governing your case. For a deeper understanding, check out our guide on leveraging AI for HR compliance in India.
Using Legal AI to Navigate Your CDA Case
Knowing the theory behind the conduct discipline and appeal rules is one thing. Applying them correctly when you’re under immense pressure is a completely different ball game. This is where the right technology can make all the difference, turning a complex, confusing procedure into a series of clear, manageable steps.
Think of a legal AI tool like Draft Bot Pro as your personal paralegal, guiding you through the practical side of things. It helps you move from just knowing the rules to actually applying them, ensuring every document you prepare is precise, compliant, and professionally drafted. It makes expert-level assistance accessible to everyone, not just those with deep pockets.
If you're an employee facing disciplinary action, the AI becomes a powerful ally. It can walk you through creating a point-by-point reply to a show-cause notice, making sure no allegation is accidentally ignored. When it’s time to appeal, it helps you construct a solid, comprehensive memo from scratch, articulating your case logically and persuasively.
For Management and HR Professionals
The stakes are just as high for management. One small procedural mistake can get an otherwise solid disciplinary action thrown out, wasting everyone's time and undermining the entire process.
Here, Draft Bot Pro helps by generating compliant charge sheets and inquiry notices from the get-go. This drastically cuts the risk of a decision being overturned on a technicality, ensuring the process is fair and robust right from the start. Using tools for a powerful AI legal document review can also help you catch inconsistencies before they balloon into major problems.
InsightsOne of the biggest advantages of using AI is consistency. It helps ensure that similar types of misconduct are handled with the same procedural standards every single time. This consistency is a cornerstone of fairness and goes a long way in reducing claims of bias or unfair treatment across the organisation.
Making Expert Assistance Accessible
At the end of the day, legal AI closes a critical gap. It demystifies the intricate web of conduct discipline and appeal rules, giving both individuals and organisations the confidence to navigate the process fairly and correctly.
By equipping both sides with the right tools, platforms like Draft Bot Pro help foster a more transparent and just workplace. To see how this tech is changing the game for legal work, you can learn more about how an AI legal assistant in India can support your specific needs. It ensures that every action is built on a solid procedural foundation, strengthening the integrity of the entire disciplinary process.
Common Questions About Discipline and Appeal Rules
Getting your head around the tangle of conduct, discipline, and appeal rules can be tricky. It often throws up a lot of practical questions. Let's walk through some of the most common ones to give you clear, direct answers so you know exactly where you stand.
Suspension vs. Penalty: What's the Difference?
A lot of people mix these two up, but they are worlds apart. Suspension isn't a punishment. Think of it as a temporary time-out. It’s a precautionary step an employer takes to keep someone away from the office while a disciplinary inquiry is happening, making sure the investigation can run smoothly without any interference.
A penalty, on the other hand, is the actual punishment that comes after the inquiry is over and the charges have been proven. This is the real consequence, and it can be anything from a simple warning all the way to dismissal.
Can I Be Dismissed for a Minor Offence?
In a fair system, this is almost impossible. There's a fundamental concept in disciplinary action called the 'principle of proportionality'. What this means, in simple terms, is that the punishment must fit the crime.
Trying to dismiss someone for a small slip-up would be a massive violation of this principle. Actions like that are exactly what the appeal process is for, and they often get overturned.
InsightsThe appeal process is a vital safety net. It keeps the disciplinary authority's power in check. If a penalty is shockingly out of proportion to the actual offence, the appellate authority can step in, cancel the order, and either impose a lesser penalty or clear the employee entirely.
What if My Appeal Is Rejected?
If your first appeal gets shot down, don't assume it's the end of the line. You might still have options. The next step could be filing a review petition with an even higher authority inside your organisation, assuming the rules allow for it.
Once you've exhausted all the internal routes, your final port of call is the judiciary. This usually means approaching a body like the Central or State Administrative Tribunal. You could also file a writ petition in the High Court to challenge the decision on legal grounds.
If you're scratching your head wondering whether Central, State, or PSU rules apply to you, a tool like Draft Bot Pro can be a lifesaver. Its AI is built to ask you the right questions about your employer. Based on what you tell it, it figures out the correct set of rules and then helps you generate the right documents, making sure everything is procedurally sound.
Navigating these complex rules demands precision. Draft Bot Pro helps you generate accurate, well-structured legal documents, ensuring your arguments are presented effectively and in line with the correct procedures. Take the guesswork out of your legal drafting by visiting https://www.draftbotpro.com to see how it works.