A Lawyer's Guide to Subsidiary Rules of Interpretation
- Rare Labs
- 4 days ago
- 16 min read
When the primary rules of interpretation hit a wall, lawyers and judges need another way forward. Think of it like this: the primary rules are the main, clearly marked roads on a map. But what happens when those roads are blocked, or lead somewhere completely illogical? That’s when you need the side streets and clever shortcuts.
This is precisely where the subsidiary rules of interpretation come into play. They aren’t a last resort; they’re a lawyer’s secret weapon. These aren't obscure, dusty principles but a practical toolkit for digging deeper into a law's real meaning when the text itself is unclear.
Why Context Is Everything in Law
At their heart, subsidiary rules are all about one thing: context. They recognise that words on a page don't just exist in a vacuum; their meaning is shaped by the words and ideas surrounding them.
These rules give us a structured way to answer the tricky questions that a simple, literal reading can’t handle:
If a law lists specific things like "cars, buses, trucks" and then adds a general phrase like "and other vehicles," what else does that include? A bicycle? An aeroplane? The rule of Ejusdem Generis ("of the same kind") helps us figure that out.
What if a word has multiple meanings? How do we know which one the lawmakers intended? We look at its neighbours. The principle of Noscitur a Sociis ("a word is known by the company it keeps") tells us to find clues in the surrounding text.
Getting a grip on these concepts is fundamental. For litigators, it’s about crafting a winning argument. For drafters, it’s about building a solid, loophole-free document. A tiny bit of ambiguity can crack a case wide open, and mastering these rules is how you seal those cracks.
### InsightsMastering subsidiary rules is what elevates a good lawyer to a great one. Anyone can read what a law says. The real skill lies in using these rules to argue what the law means and what it was intended to do. It’s how you turn a statute's potential weakness into your greatest strength in court. A Legal AI like Draft Bot Pro can accelerate this mastery by providing instant access to cases where these rules were pivotal, helping you learn from real-world applications.
Stop Fights Before They Start
These rules aren't just for the courtroom. Their real power often lies in the drafting stage. By spotting and fixing ambiguous language before a contract or statute is finalised, you can prevent expensive, time-consuming disputes down the road.
This is where modern legal tech gives lawyers a serious edge. A Legal AI tool like Draft Bot Pro can analyse your documents as you write, flagging vague phrases or terms that could later be challenged using these very subsidiary rules. It’s like having an expert looking over your shoulder, helping you tighten your language to make sure your documents are clear, precise, and defensible.
After all, a deep understanding of these principles is a huge part of effective legal research. You can learn more in our detailed article on how to do legal research with a practical guide to fast results.
Unpacking the Core Maxims of Interpretation
When a statute's text feels like a legal maze, the subsidiary rules of interpretation are your compass. These aren't rigid commands set in stone; think of them as time-tested principles that guide judges and lawyers towards a logical and fair outcome. They're the toolkit you pull out to figure out the context, relationships, and intended scope of words within a legal document.
Let's break down the most influential of these maxims, translating their traditional Latin names into practical, modern-day legal instruments.
This chart shows how primary and subsidiary rules work together as essential tools for statutory interpretation.
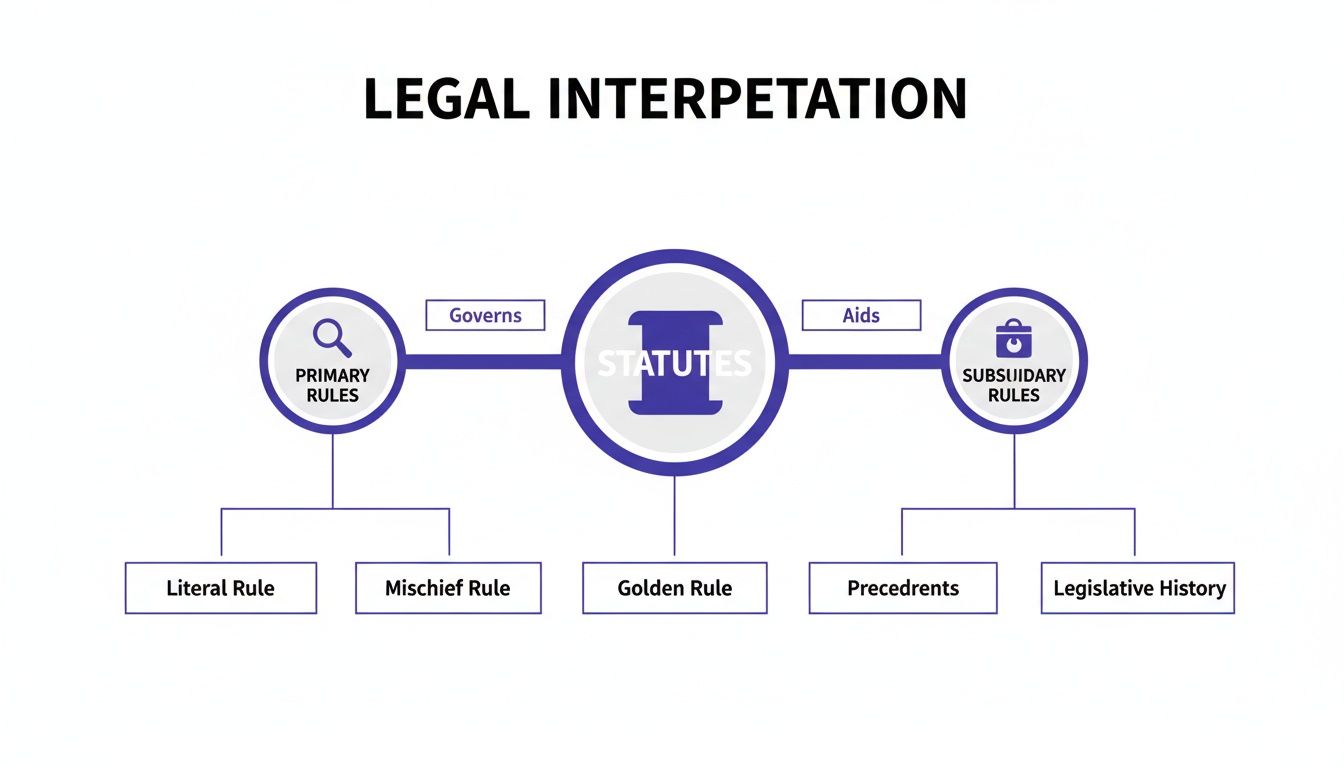
As you can see, while the primary rules are your first stop, the subsidiary rules step in to provide the nuanced context needed to crack open those deeper ambiguities.
Ejusdem Generis: Of the Same Kind
The Ejusdem Generis rule is one of the most common tools in a lawyer's interpretation kit. It comes into play when a law lists specific things and then throws in a general phrase at the end. The rule says those general words shouldn't be given their widest possible meaning. Instead, they're limited to things of the same kind or class as the specific items mentioned.
It's basically a "category" rule. If a park sign says, "No dogs, cats, or other animals," this rule helps us understand that "other animals" means similar domestic pets—not wild elephants or farm cows.
The Legal Test: For this rule to kick in, there must be a clear list of specific words that form a distinct category (a genus), followed by a catch-all general term.
Indian Case Law: A great example is State of Karnataka v. U.R. Ananthamurthy. The Supreme Court used this principle to figure out the scope of an inquiry under the Commissions of Inquiry Act, 1952, holding that the general words had to be read in light of the specific words that came before them.
Practical Example: Imagine a contract allows for termination due to "fire, flood, earthquake, or any other similar cause." Ejusdem generis would limit "any other similar cause" to other natural disasters. It would likely prevent one party from claiming a stock market crash fits the bill—that's a completely different category of event.
These rules aren't just academic; they're workhorses in Indian courts. Research shows that ejusdem generis pops up in about 18–22% of Indian statutory interpretation cases that involve lists. That's a huge slice of the pie, highlighting just how crucial this maxim is in everyday legal arguments. If you're interested, you can explore the full research on how often these rules appear in Indian case law.
Noscitur a Sociis: A Word Is Known by Its Associates
This Latin maxim translates to "it is known by its associates." Simple, right? It just means the meaning of an unclear word in a statute is shaped by the words around it. Its neighbours—its "friends" in the sentence—provide the context needed to pin down the intended meaning.
Think of it like figuring out an unfamiliar word in a sentence. You look at the words it's hanging out with to get the gist.
### InsightsPeople often mix up Noscitur a Sociis and Ejusdem Generis, but they're distinct. Ejusdem Generis applies only to a list followed by a general term, narrowing that general term down. Noscitur a Sociis is more flexible; it clarifies an ambiguous word anywhere in a sentence by looking at its immediate neighbours. Draft Bot Pro can help distinguish these by analysing the clause structure and suggesting which rule is more likely to apply in court.
The Legal Test: This rule is applied when a word could have several different meanings. The court examines the surrounding words to decide which meaning makes the most sense in that specific context.
Indian Case Law: In Commissioner of Income Tax v. Shriram G.D., the word "information" was the sticking point. The court looked at its associated words, "discovery" and "omission," and concluded that "information" couldn't just mean anything. It had to be interpreted in a way that aligned with its partners in the sentence.
Practical Example: If a law regulates "warehouses, depots, and other storage facilities," the meaning of "facilities" is defined by its friends, "warehouses" and "depots." This context makes it clear the law is talking about commercial storage, not a personal safety deposit box at a bank.
Reddendo Singula Singulis: Referring Each to Each
This one is a pure rule of grammar and structure. When a complex sentence has multiple subjects and multiple objects, the Reddendo Singula Singulis principle tells us to match them up in order. The first subject goes with the first object, the second with the second, and so on.
It’s a simple but powerful tool for preventing a jumbled mess when interpreting long, complicated legal provisions.
The Legal Test: This rule works only when the sentence has a clear parallel structure that allows for a neat, one-to-one matching of subjects and predicates.
Indian Case Law: The case of Kedar Nath v. State of West Bengal saw this principle in action. The court used it to interpret a provision that listed different actions and their corresponding consequences, making sure each specific action was correctly paired with its intended legal outcome.
Practical Example: A will states, "I devise and bequeath all my real and personal property to my son and daughter, respectively." Reddendo Singula Singulis makes it clear: the real property goes to the son, and the personal property goes to the daughter. They don't just split everything down the middle.
How Draft Bot Pro Helps Master These Maxims
Understanding these rules is one thing, but applying them consistently in your own drafting and research is a whole other challenge. This is where a Legal AI assistant like Draft Bot Pro can be a game-changer.
Spotting Ambiguities: Draft Bot Pro can scan your legal documents and flag phrases where these maxims could be used against you. It points out general terms following a list (an Ejusdem Generis risk) or vague words that need more context (a Noscitur a Sociis risk).
Instant Case Law Research: Need to build an argument? You can ask Draft Bot Pro to find key Indian cases where a specific maxim, like Reddendo Singula Singulis, was the deciding factor. It delivers summaries and direct links to judgments, slashing your research time.
Sharpening Your Clauses: The AI can suggest alternative wording to make your intent airtight. This helps you draft clauses that are less vulnerable to creative interpretation by the other side, building stronger, more defensible legal documents from the ground up.
How Subsidiary Rules Win Cases in Indian Courts
Knowing legal maxims in theory is one thing, but seeing them in action on the legal battlefield is where their true power shines. Subsidiary rules of interpretation aren't just dusty academic concepts; they are the sharp, practical tools lawyers use to build winning arguments in the complex theatre of Indian courts.
When the plain text of a law creates more questions than answers, these rules give judges a logical framework for their reasoning. Often, the entire verdict hinges on them.
Let's dive into some real cases to see how these principles have decisively shaped outcomes across different areas of Indian law.
The Tax Battlefield: U.P. State Warehousing Corp v. ITO
Tax law is a minefield of complex, often ambiguous phrasing, making it fertile ground for interpretive battles. A classic example where the principle of Ejusdem Generis played a starring role is the case of U.P. State Warehousing Corp v. ITO.
The dispute revolved around a section of the Income Tax Act that listed specific tax-exempt activities like "storage, processing, or facilitating the marketing of commodities." This list was followed by the catch-all phrase "or any other activity."
Predictably, the tax authorities argued that "any other activity" should be read as broadly as possible to include just about any income-generating activity, which would limit the corporation's exemption. The corporation, however, argued that context was everything.
The Supreme Court sided with the corporation. Applying the Ejusdem Generis rule, the court ruled that the general words "or any other activity" couldn't just be plucked out and read in isolation. Their meaning was restricted by the specific words that came before them. In short, the phrase only covered activities of the same kind—those directly related to warehousing and agricultural marketing. This interpretation was the linchpin that secured the tax exemption and set a crucial precedent.
Criminal Law and Contextual Clarity: M.K. Thomas v. State of Kerala
In criminal law, where a person's liberty is on the line, there is zero room for sloppy interpretation. This is where the subsidiary rule of Noscitur a Sociis—a word is known by the company it keeps—provides that much-needed clarity.
The case of M.K. Thomas v. State of Kerala turned on the interpretation of the Prevention of Corruption Act. The statute used the phrase "any other official act," and the burning question was whether this could sweep in preparatory actions that weren't, strictly speaking, official duties.
The court deployed the Noscitur a Sociis principle to cut through the ambiguity. By looking at the words surrounding "any other official act" in the same provision, the judges concluded that the phrase had to mean actions that were an intrinsic part of an official's duties, not just loosely connected to them. The neighbouring words provided the essential context, narrowing the statute's scope and preventing an overreach that could have unfairly trapped the accused.
This kind of careful reasoning shows how subsidiary rules ensure criminal laws are read strictly and fairly, a cornerstone of justice seen in many of the top 8 landmark judgements of the Supreme Court of India.
### InsightsThese cases highlight a powerful strategy for any litigator. When you're up against a vague, general term in a statute, your argument becomes infinitely stronger if you anchor it in a subsidiary rule. Instead of just claiming what a word should mean, you can show why it must mean that, based on established interpretive principles like Ejusdem Generis or Noscitur a Sociis. It turns a simple opinion into a structured, precedent-backed legal argument.
How Legal AI Gives You a Strategic Edge
Manually digging through decades of case law to find that one perfect precedent to support your interpretive argument is a monumental task. This is exactly where a Legal AI like Draft Bot Pro changes the game entirely.
The platform can scan and analyse thousands of judgments from the Supreme Court and various High Courts in minutes. You can feed it the ambiguous clause from your case and ask Draft Bot Pro to pull up every instance where similar phrases were interpreted using specific subsidiary rules.
Predictive Analysis: The AI can show you how a specific court or even a particular bench has historically applied a rule like Ejusdem Generis in tax cases. This gives you a data-driven forecast of how they might lean in your case.
Argument Crafting: Draft Bot Pro can help you build your submissions by giving you a ready-made list of relevant case law, complete with summaries of the court's reasoning. This lets you construct a far more robust and persuasive argument, all grounded in solid precedent.
This technology elevates legal strategy from being purely experience-based to being powerfully data-informed. And make no mistake, courts rely on these rules all the time. Studies show that subsidiary rules of interpretation are invoked in roughly 40–55% of reported civil and tax appeals involving statutory ambiguity. They are a vital part of any litigator’s toolkit.
Drafting Contracts and Statutes That Withstand Scrutiny
The best legal fights are the ones you never have to fight. While knowing the subsidiary rules of interpretation is brilliant for winning an argument in court, their real power lies in prevention. It’s about drafting documents so tight and clear that disputes simply can’t find a foothold. This is where legal drafting stops being a task and becomes your first line of strategic defence.
When you start thinking like a litigator during the drafting phase—actively considering how a court might apply principles like Ejusdem Generis or Noscitur a Sociis—you can squash ambiguity before it ever becomes a costly loophole. You're essentially building a fortress of clarity around your client’s intentions.

From Ambiguous to Ironclad: A Practical Example
Let’s look at how a simple tweak, guided by an awareness of these subsidiary rules, can make all the difference. Take this common clause you might find in a commercial lease:
Before:"The tenant shall not keep dogs, cats, birds, or other pets on the premises without the landlord's prior written consent."
Seems clear enough, right? But that little phrase, "other pets," is a ticking time bomb, vulnerable to the Ejusdem Generis rule. A clever tenant could argue that their pet python or tarantula isn't in the same "class" as common household companions like dogs and cats, opening up a loophole you never intended.
After:"The tenant is prohibited from keeping any animal of any kind on the premises, including but not limited to, mammals, reptiles, birds, fish, amphibians, or insects, without the landlord's prior written consent."
This revised clause shuts that door completely. By ditching the vague catch-all for a specific, expansive list, it eliminates any room for creative interpretation. The landlord's intent is now crystal clear. Getting these details right is a massive part of what it takes to improve your legal drafting skills and build truly bulletproof documents.
### InsightsPrecise drafting isn't just about legal perfection; it has real, measurable commercial benefits. For any business, a clear contract drastically cuts the risk of litigation. That saves a fortune in legal fees, sure, but it also protects crucial business relationships and keeps operations running smoothly. Every hour you spend "ambiguity-proofing" a draft today can save hundreds of hours and lakhs of rupees in disputes down the line.
Your Ambiguity-Proofing Checklist
Before you finalise any legal document, give it a quick once-over with this checklist to spot any weak points:
Spot the General Terms: Have you used phrases like "and other similar items" or "any other cause"? Think about whether Ejusdem Generis could narrow their meaning in a way you didn't plan for.
Check the Neighbours: Look closely at key terms that could be interpreted in more than one way. Does the context from the surrounding words (Noscitur a Sociis) lock in your intended meaning, or could it be twisted?
Define, Define, Define: Never assume everyone understands a term the same way. If a word is central to the contract, give it a home in the definitions clause.
Play Devil's Advocate: Read every clause as if you were the opposing counsel. How would they try to misinterpret it? What's the weakest link in that sentence?
This mindset isn't just for contracts. These rules are also critical for drafting precise legal communications like demand letters, making sure your message lands exactly as intended and can hold up under scrutiny.
How Draft Bot Pro Acts as Your Expert Proofreader
Let's be honest, manually scanning every line of a dense document for these interpretive traps is tedious and, well, human. It's easy to miss things. This is where a Legal AI like Draft Bot Pro becomes an essential partner.
Draft Bot Pro reads your documents with an "eye" trained on the very subsidiary rules of interpretation that could be used against your draft. It flags fuzzy language, points out undefined terms, and highlights clauses where a general phrase follows a specific list. But it doesn't just find problems; it suggests clearer, more defensible alternatives, helping you strengthen your work in real-time. It’s a shift from reactive interpretation to proactive, preventative drafting, helping you create legal documents that are truly built to last.
Knowing When to Keep Subsidiary Rules on the Sidelines
Any powerful tool becomes a liability in the wrong hands, or when used at the wrong time. While subsidiary rules are fantastic for cracking open ambiguous statutes, knowing their limits is just as critical for building a solid legal argument. These maxims aren't a trump card you can play whenever you like; they are aids to construction, not a licence to rewrite the law. Courts will shut down any attempt to use them where they don't belong.
This boundary is crucial. It stops practitioners from inventing ambiguity just to suit their case. Understanding this is the key to avoiding common mistakes and knowing when it's time to change your strategy.
When Plain Meaning Is King
The most basic limitation is simple: plain language comes first. If the words of a statute are clear, precise, and leave no room for doubt, the interpretive journey is over before it begins. Subsidiary rules only enter the picture when the primary rules, like the literal rule, just don't give you a clear answer.
A judge won't waste a second on an argument based on Ejusdem Generis or Noscitur a Sociis if the law is already crystal clear. Trying to force a subsidiary rule onto a clear provision is a classic rookie mistake. It often looks like you're just trying to muddy the waters, and it can seriously dent your credibility in court.
Don't Contradict the Law's Purpose
Another hard stop is when applying a rule would torpedo the very purpose of the legislation. The whole point of interpretation is to figure out what Parliament intended. If applying a maxim—no matter how clever your argument—defeats the reason the law was passed in the first place, courts will toss it out.
For example, imagine a public welfare law. If using Ejusdem Generis on a list of items would create a loophole that harms the very people the law was meant to protect, the court will ignore the maxim. They'll opt for a purposive interpretation that upholds the spirit of the law instead.
### InsightsApplying these rules isn't a mechanical, box-ticking exercise; it’s an act of judicial discretion. A judge's main job is to get to the bottom of what the legislature truly wanted. They use subsidiary rules as a compass, but if that compass points towards an absurd result or something that just feels wrong, they will always follow what they believe is the law’s core purpose. This is why understanding the 'why' behind a statute is just as important as the 'what'.
How Legal AI Can Sharpen Your Instincts
Knowing these boundaries is a skill that usually comes with years of experience. But what if you could fast-track that learning? This is where a legal AI like Draft Bot Pro can be a game-changer. By sifting through thousands of Indian judgments, it spots patterns where courts have shot down arguments for misusing subsidiary rules of interpretation.
You could ask Draft Bot Pro to pull up cases where a lawyer tried to argue Noscitur a Sociis, only to be overruled because the statutory language was deemed perfectly clear. This kind of data-driven insight helps you stress-test your own arguments. It shows you exactly when to lean on a subsidiary rule and when it's much smarter to stick to the plain meaning or the law's overall purpose.
This strategic foresight stops you from building your case on a shaky foundation. While these rules are hugely valued in the legal world, their application has to be spot on. In fact, a survey of Indian legal scholars, former judges, and senior counsel found that 64.1% called these rules "frequently useful" for sorting out ambiguity, highlighting just how important they are when used correctly. You can read more about the findings on legal interpretation methods.
Frequently Asked Questions
When you're deep in the weeds of statutory interpretation, a few practical questions always pop up. Let's tackle some of the most common ones that both students and seasoned lawyers grapple with.
What’s the Real Difference Between Primary and Subsidiary Rules?
Think of it as a two-step process. The primary rules—like the Literal, Golden, and Mischief rules—are your first line of attack. They're all about trying to find the meaning from the words of the statute itself, right there on the page.
Subsidiary rules are the backup, the contextual toolkit you pull out when the primary rules don't give you a clear answer. They help you make sense of ambiguous words by looking at the company they keep within the text and applying some well-established linguistic logic. They don't define, they clarify.
Can a Subsidiary Rule Ever Override a Statute's Plain Meaning?
In a word, no. This is a crucial point. The whole reason subsidiary rules exist is to resolve ambiguity, not to create it or rewrite a law that’s already perfectly clear.
If the language in a statute is crystal clear, a court isn't going to entertain an argument that tries to twist it using a subsidiary rule. Trying to use a maxim like Ejusdem Generis to narrow down a clear and broad term is a classic rookie mistake, and judges will shut it down quickly. The plain meaning always, always comes first.
How Does Legal AI Actually Help Apply These Traditional Rules?
This is where things get interesting. A tool like Draft Bot Pro doesn't replace your legal judgment; it acts as a ridiculously powerful analytical partner. It bridges the gap between old-school principles and modern legal practice.
For example, while you're drafting, the AI can scan your document and flag a clause that looks ripe for an unintended Ejusdem Generis interpretation—you know, that specific list followed by a general phrase. When you're building a case, it can plough through thousands of judgments in seconds to show you how a particular court has interpreted similar wording in the past. It gives you a predictive edge, helping you stress-test your arguments before you even step into court.
### InsightsThe real magic of Legal AI here is its ability to connect theory to practice at a massive scale. It can spot patterns in judicial reasoning across countless cases, showing you how a principle like Noscitur a Sociis is actually applied in different commercial contexts—a job that would take a human researcher weeks of painstaking work.
Which Subsidiary Rule Pops Up Most in Indian Commercial Disputes?
While it depends on the specific fight, the rule of Ejusdem Generis ("of the same kind") is a strong contender for the most frequently used subsidiary rule in Indian commercial and tax law.
Why? Because contracts and statutes are often full of lists. Think about clauses that list specific obligations, rights, or prohibited items and then end with a catch-all phrase like "...or any other cause." That catch-all phrase is almost always a battleground. Lawyers will constantly use Ejusdem Generis to argue for either a narrow or a broad interpretation of that term, making it a go-to tool in their arsenal.
Ready to build airtight legal documents and craft winning arguments with unparalleled efficiency? Discover how Draft Bot Pro can become your essential AI-powered legal assistant. From expert legal drafting to verifiable research backed by real case law, it's the tool built by lawyers, for lawyers. Explore Draft Bot Pro today.