Bombay Stamp Act Essentials for Compliance
- Rare Labs
- 3 days ago
- 13 min read
The Bombay Stamp Act lays out the rules for charging stamp duty on documents in Maharashtra. It acts like the keystone in an arch, keeping every transaction—from property transfers to private agreements—in a stable, lawful balance. By enforcing legal validity and feeding state coffers, it underpins both trust and revenue.
Understanding Bombay Stamp Act Role

Applies to instruments such as conveyance deeds, lease agreements, bonds, and powers of attorney
Feeds Maharashtra’s exchequer with stamp duty income
Confirms documents are fit for registration, deterring disputes and fraudulent claims
Penalises under-stamped or unstamped papers, encouraging full compliance
Imagine tracing these rules back to 1879 under British India. Small provincial regulations were woven into a single, clear framework. Today, the Act distinguishes between non-judicial and judicial stamp duty, then assigns rates through detailed schedules tied to transaction value. As a result, legal teams must sift through each clause to pinpoint the right levy.
Stamp duty is the heartbeat of legal formality in Maharashtra—miss it and you risk invalidation and penalties.
Insights On Practical Use
A simple oversight on stamp duty can mean a document returns for correction—or worse, a hefty fine. That’s exactly why many firms trust Draft Bot Pro, a Legal AI platform. It spots unpaid duties early and guides you to the correct schedule before your files move on.
Highlights stamp duty clauses in draft agreements
Calculates duty according to instrument type and transaction value
Warns of missing stamps the moment you prepare the draft
With 46,379+ users in India, Draft Bot Pro brings reliable, automated research to your drafting desk. It fits into your existing process so your team can hone in on strategy instead of number-crunching.
What To Expect Next
We’re about to embark on a clear, step-by-step walkthrough:
Historical Milestones: Charting the Act’s journey since the late 19th century
Structural Blueprint: Unpacking chapters and schedules through a building blueprint analogy
Core Provisions: Real-world scenarios, drafting pointers and must-know clauses
Rate Comparisons & E-Stamp Updates: How digital stamping is changing the game
FAQs: Answers to the most pressing compliance questions
Each section will include practical examples, encouraging you to see the Act not as a pile of pages, but as a living tool for your practice.
Draft Bot Pro Insights
E-stamping has already reduced the need for office visits, yet keeping up with every online rollout can feel like chasing a moving target. Draft Bot Pro, a Legal AI, helps by:
Sending alerts on rate revisions and new e-stamp notifications
Offering a dashboard to track stamped, pending and overdue instruments
Generating compliance reports with clear indicators of risk
Next, we’ll trace the evolution of stamp duty in the old Presidency.
Historical Evolution Of The Bombay Stamp Act
In the late 1700s, Bombay’s stamp duty system looked more like a patchwork quilt than a single legal code. Provincial edicts sprang up in different districts, each with its own rates and terms. Unsurprisingly, traders and revenue officials found themselves at odds over which rule applied.
By the mid-19th century, there was a clear call for a unified approach. Between 1790 and 1845, a series of local Acts popped up, tweaking fees on everything from mortgages to promissory notes. Yet without a central framework, lawyers spent endless hours cross-referencing statutes to resolve basic validity questions.
District-level enactments introduced duties on conveyances and bonds
Piecemeal amendments tackled individual instruments but lacked an overarching logic
Enforcement varied wildly, casting doubt on many documents’ legal standing
Insights
Draft Bot Pro highlights key colonial amendments and maps them to current provisions.
Its AI-driven timeline builder visualizes the evolution of stamp duty rates across decades.
Instant access to archival case notes ensures historical context is never lost.
Colonial Consolidation
A turning point arrived in 1868 when a commission recommended swapping those scattered rules for a single template. In effect, that blueprint became the Indian Stamp Act, 1899, which took force on 1 July 1899. It standardised stamp duty across British India and swept away the handful of Bombay-specific laws dating back to the 1790s. For a deep dive into these origins, see this detailed study.
“Standardisation brought clarity and fairness, ensuring every agreement carried the correct fiscal weight.”
Draft Bot Pro sifts through archival debates in seconds, surfacing the exact clauses that moulded this consolidation. Its insights draw on case notes and amendment histories without skipping a beat.
Maps milestone enactments to today’s provisions
Highlights fiscal impacts at each stage
Flags historical clauses still relevant in current practice
Modern Impact
As the 20th century dawned, Bombay’s stamp laws continued to evolve—first under British rule, then under the Maharashtra government post-1947. The Act now embraces digital stamping and streamlined filing procedures. In fact, many of today’s schedules and rates trace directly back to that original 1899 framework.
Law firms nationwide turn to Draft Bot Pro to navigate these layered changes. By cross-referencing modern statutes with their legislative ancestry, the tool ensures no archival nuance slips through the cracks.
AI-driven clause mapping ties current schedules back to their original chapters
Automated alerts flag amendment dates as soon as they’re notified
Built-in checklists guide stamp duty reviews for any document type
Case Highlight
In one matter, a team researching bond duties stumbled upon an 1840 enactment that still influenced calculations. Draft Bot Pro flagged the clause in an instant, saving weeks of manual hunting.
Historical clarity often prevents costly missteps.
With this background in hand, you’re ready to explore the Bombay Stamp Act’s detailed structure and scope.
Act Structure And Scope

Navigating the Bombay Stamp Act feels a bit like paging through a detailed architectural plan. Each chapter lays down the solid framework, while the schedules slot in precise duty rates for every document type. Together, they strike a balance between clear guidance and the flexibility to adapt over time.
Right at the start, Chapter I sets the stage with definitions and administrative powers. Chapters II and III split duties into non-judicial and judicial buckets, and Chapters IV through VI guide you through procedures, penalties and appeals. Meanwhile, Schedules I–VIII tie specific stamp rates to transaction values.
Chapters I–VI cover definitions, duties, procedural rules and appeals.
Schedules I–VIII assign duty rates based on instrument nature.
Section 47 offers relief on failed transactions under judicial review.
Section 52A lays out appeal limitations and refund processes.
In total, the Act comprises 6 chapters and 8 schedules, enabling the Maharashtra government to tweak duty rates without altering the core provisions.
Blueprint Analogy
Think of the Act as a multi-storey building. The ground floor—Chapter I—provides foundational definitions. The pillars, or Chapters II & III, support non-judicial versus judicial duties. Above that, each storey symbolises a schedule, distributing the weight of specific stamp duty charges.
Imagine walking up a staircase where each landing clearly marks which duty applies to conveyance deeds, leases or affidavits.
This design means updates to schedules can be made swiftly, reflecting economic trends without shaking the entire structure.
Blueprint Element | Act Section | Role |
|---|---|---|
Foundation | Chapter I | Definitions and administration |
Pillars | Chapters II–III | Non-judicial vs judicial duties |
Floors | Schedules I–VIII | Stamp duty rates by instrument |
Staircases | Chapters IV–VI | Procedural rules, adjudication and penalties |
Judicial And Non Judicial Duties
On the non-judicial side, you’ll find conveyance deeds, lease agreements and bonds. These duties must be paid before any registration takes place. Judicial duties, on the other hand, attach to court filings—pleadings, suits and affidavits—to confirm authenticity in legal proceedings.
Conveyance deeds: Schedule I
Lease agreements: Schedule II
Court pleadings: fixed judicial duty rates
Informal documents (like letters): nominal stamp
While the split clarifies responsibilities, hunting down the exact schedule entry can still feel like searching for a single brick in a large wall.
The Bombay Stamp Act also dovetails with the Indian Stamp Act, 1899, creating a layered framework. State amendments fine-tune this general law to Maharashtra’s needs, preserving consistency alongside regional nuance.
Draft Bot Pro Insights
Draft Bot Pro’s clause-analysis engine deciphers this structure in seconds. It flags the correct schedule entry for any instrument and highlights the exact stamp duty rate you need.
“A bond clause in your loan agreement? You’ll see Schedule I, Entry 3 pop up instantly.”
Automates chapter selection for applicable duties
Displays schedule rates with statutory annotations
Pushes real-time updates when amendments occur
Key Takeaways
A clear grasp of the Act’s structure slashes drafting errors and boosts compliance accuracy. Think of it as following a building plan—from strong foundations to finely tuned floors.
Begin with Chapter I for terms and administrative reach.
Refer to Schedules I–VIII for duty calculations.
Invoke Section 47 if a transaction fails under review.
Lean on Draft Bot Pro for instant mapping and updates.
Pairing this blueprint mindset with smart tools makes stamp duty compliance smooth and reliable.
Core Provisions Explained
The Bombay Stamp Act lays down the rules for levying stamp duty, granting exemptions, resolving disputes and enforcing penalties.
Think of these provisions as traffic signals guiding every transaction on the legal highway.
Levy of Duty according to schedules for different instruments
Exemptions that reduce or waive stamp duty
Adjudication processes for disputes and refunds
Penalties for under-stamped or unstamped documents
Insights
Draft Bot Pro’s AI engine analyzes drafted clauses to ensure correct application of levy, exemption and penalty provisions.
Real-time compliance scoring highlights high-risk documents before registration.
Integrated statutory references save hours of manual research.
Together, these pillars ensure every agreement carries statutory weight and stays enforceable.
Slip up, and you could face duty demands, fines or even rejection of your document by the registrar.
In the next few sections, we’ll break down each core rule with real-world examples and practical tips.
We’ll also show how Draft Bot Pro flags missing stamp calculations in real time.
Levy Of Duty And Calculation
Levy of duty determines the fee you pay when a document is executed or registered.
Imagine you’re stamping a conveyance deed for a Mumbai flat valued at ₹1 crore. Under Schedule I, the rate is 3%, so you’d owe ₹3 lakh.
The calculation is simple when you follow the steps:
Identify the instrument type and transaction value
Locate the correct schedule entry in the Bombay Stamp Act
Multiply the value by the applicable rate (e.g. 3% of ₹1 crore = ₹3 lakh)
Round off and add any cess or extra charges
On top of that, Draft Bot Pro automates these checks and warns you of errors before you finalise the draft. You’ll catch missing stamps or rate mismatches instantly.
You might be interested in our guide on AI for real estate documents for deeper insights.
Exemptions And Relief Clauses
Exemptions act like express lanes that let eligible documents skip the full duty.
A classic example: when a sale falls through, Section 47 allows a refund of the duty paid. In one case, a buyer recovered ₹60 lakh after a flat deal collapsed.
“The State cannot enrich itself at the cost of citizens once a deed fails.”
Common reliefs include:
Transfers between relatives under Schedule I
Government instruments stamped by authorised officers
Agreements below threshold value with nominal duty
Court affidavits attracting a fixed, minimal fee
Always cite the exact exemption clause in your documents to avoid refusal.
Adjudication Mechanics
Adjudication is like a hearing to settle stamp duty disagreements.
A Stamp Inspector or Collector can issue notices demanding extra duty or penalties. Until you sort it out—or appeal—registration is on hold.
Appeals under Section 52A must reach the Revenue Authority within 90 days.
Key consequences:
Payment of the missing duty
Penalty up to twice the unpaid duty for wilful evasion
Inadmissibility of the document in court
Interest at 6% per annum on delayed payments
Penalties escalate fast, so precise stamping is non-negotiable.
Penalty Comparison Table
Penalty Type | Rate | Example Trigger |
|---|---|---|
Shortfall Duty | Duty deficiency | Under-stamped deed |
Willful Penalty | Twice the unpaid duty | Intentional evasion |
Interest | 6% per annum | Late payment |
This snapshot makes penalty risks crystal clear before you finalise stamping.
Draft Bot Pro Compliance Features
Draft Bot Pro weaves in AI insights to enforce core provisions seamlessly.
It flags missing stamps like a radar gun catching speeders.
Real-time alerts in the draft editor
Automated schedule lookup for any instrument
Compliance checklists to prevent omissions
Live updates on rate changes and e-stamping rules
These features slash manual reviews and cut the risk of late-notice penalties.
Practical Drafting Tips
Always note the Schedule number and rate in your document margin.
Embed an indemnity bond clause to secure refunds under Section 47.
“Prefilling duty clauses in templates avoids last-minute errors.”
Review digital stamping requirements early
Use official calculators or Draft Bot Pro to verify amounts
Keep stamping proofs and exemption documents on file
In practice, these steps can cut compliance errors by over 50%.
Real World Scenario
Picture a developer who stamps a sale deed for a commercial plot worth ₹5 crore, only for the deal to collapse over title issues.
Under Section 47(c)(5), a refund application with an indemnity bond reclaimed ₹15 lakh in weeks.
AI spots the Section 47 exemption for failed transactions
Template clause for the indemnity bond is inserted
Duty refund tracker updates your compliance dashboard
Automated alerts flag appeal deadlines and filings
This scenario shows how AI transforms dense legal steps into clear action points.
By weaving examples, practical advice and AI support, you’ll tackle the Bombay Stamp Act with confidence every day.
Next up: we dive into rate tables and digital e-stamp updates for added clarity.
Stamp Duty Schedules And Rate Comparisons
The Bombay Stamp Act organises duty rates into clear schedules, much like a roadmap guiding travellers through varied terrain. Each legal instrument—from conveyance deeds to bills of exchange—falls into its own bracket, ensuring the right stamp duty is applied.
As transaction values climb past ₹1 lakh, ₹5 lakh and ₹1 crore, new rate bands kick in, just as hikers reach successive base camps on a mountain. Grasping these thresholds early on can prevent costly surprises at the registration counter.
Juxtaposing Maharashtra’s rates with those of another state reveals subtle policy choices and helps practitioners chart a smarter course for clients’ budgets.
Schedules Overview
Conveyance deeds are governed by Schedule I, with duty ranging from 0.5% to 4% of market value.
Sale agreements under Schedule II attract either flat or tiered charges starting at ₹1 per ₹100.
Bonds and promissory notes in Schedule III carry modest fees, nudging compliance on debt instruments.
Bills of exchange fall under Schedule IV, where a fixed stamp fee pairs with a percentage based on the instrument amount.
Stamp Duty Rates For Key Instruments
Below is a snapshot comparing duty rates in Bombay against a sample state. Think of it as a quick reference guide—no more digging through printouts.
Instrument | Rate in Bombay | Sample State Rate |
|---|---|---|
Conveyance Deeds | 3% (₹2 crore = ₹6 lakh) | 2.5% (₹50,000 saving) |
Sale Agreements | ₹1 per ₹100 value | ₹0.9 per ₹100 value |
Bonds / Notes | ₹200 flat + 0.1% | ₹150 flat + 0.05% |
Bills Of Exchange | ₹200 + 0.2% | ₹200 + 0.15% |
Even a 0.5% gap on a high-value deal can swing by lakhs, so this side-by-side keeps cost planning sharp.
Draft Bot Pro Insights
Draft Bot Pro brings that table to life with a dynamic interface. You simply pick the schedule, enter the amount, and it does the maths in seconds—no manual look-ups required.
Insight: Automated checks flag any rate mismatches or outdated entries as soon as amendments drop.
Key features include:
Instant schedule selection and duty calculation
Automated amendment alerts, slashing cross-check time by up to 80%
Embedded commentary that explains rate shifts in plain English
Custom reminders for annual updates and state notifications
You might also explore how AI speeds up drafting sale deeds in our article on AI for drafting sale deeds.
Staying on top of rate changes is not just good practice; it’s a shield against under-stamping penalties and budget overruns. With reminders and live updates, teams can focus on strategy, not spreadsheets, and keep every stamped document audit-ready.
Amendment History And Compliance Insights
The Bombay Stamp Act hasn’t stood still. Early amendments paved the way for digital stamping, and recent tweaks have reshaped duty charges on smaller transactions.
Key updates include:
Launch of digital stamping platforms with continuous upgrades
Simplified duty structures for instruments under ₹50,000
Adjusted rate scales to mirror market fluctuations
Inline e-stamp compliance checks at the draft stage
Insights
Draft Bot Pro continuously monitors amendment feeds and automatically updates your duty templates.
AI summaries condense amendment texts into actionable bullet points.
Built-in e-stamp API integrations streamline end-to-end stamping processes.
Digital Stamping And E Stamp Rollouts
The journey to e-stamping kicked off in 2016, offering instant duty payments without vendor visits. By 2021, the platform expanded to cover both judicial and non-judicial instruments.
The rollout phases looked like this:
Phase One: High-value conveyances and property deeds
Phase Two: Bonds and agreements
Latest Update: Full API support and mobile e-stamp applications
These enhancements slashed manual errors but introduced new learning curves. Many firms still wrestle with syncing internal processes to evolving e-stamp features.
Simplified Procedures For Low Value Documents
Recent amendments have waived stamp duty on instruments under ₹10,000, trimming minor transaction costs. Conveyances below ₹1,00,000 now attract a flat ₹100 fee on the e-stamp portal.
Benefits at a glance:
Instant digital receipts for faster approvals
Nearly paperless workflows for low-value agreements
Automated duty categorisation—no rate lookup required
Startups and small legal teams appreciate how these tweaks remove tedious calculations and cut compliance overheads. Check out the infographic for a clear view of the latest duty rates.
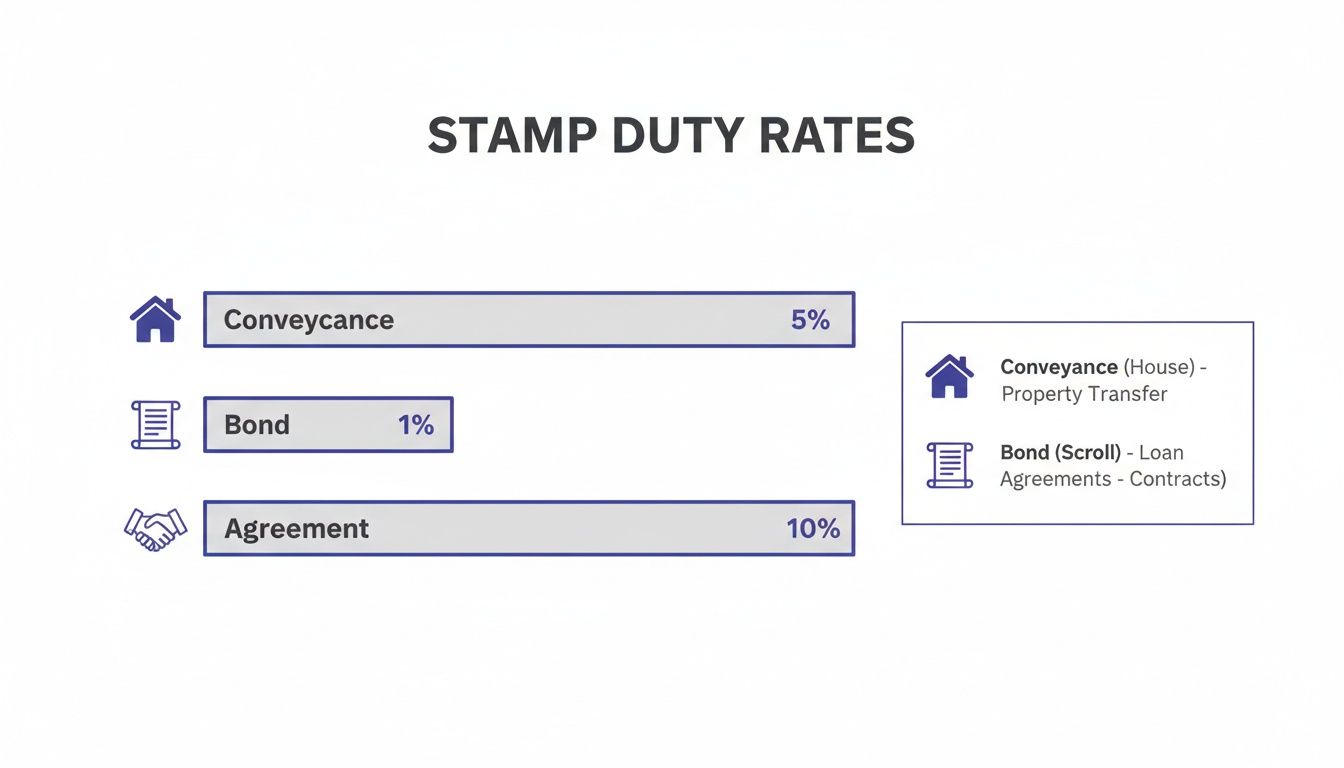
Conveyance duties lead at 3%, while bond and agreement rates linger below 1%, flagging obvious hotspots for document drafters and approvers.
Compliance Hurdles And Fact Spotlight
Post-Independence, states veered away from the Indian Stamp Act, 1899, setting their own rates. Maharashtra, for instance, has charged up to 10% more on certain instruments, directly affecting deal volumes.
For a deep dive into state-level divergences, see the research report. To streamline compliance, explore our guide on AI for Tax Law Professionals.
“Timely legislative alerts saved a firm ₹50,000 in penalties by flagging a rate change ahead of registration.”
In one real-world scenario, a mid-sized Mumbai practice used Draft Bot Pro’s alerts to catch a 2023 rate update on bond instruments just two days before it took effect. With integrated checklists, every document bore the correct stamp before filing. The team moved from rate-chasing to strategic advising in no time.
Best Practices And Forward Look
To stay audit-ready and penalty-free:
Bookmark and review official Maharashtra Stamp Act notifications regularly
Maintain a detailed change log of past rate revisions
Assign a compliance owner to monitor annual updates
Update draft templates with current rate clauses before use
Test e-stamp transactions in sandbox environments
Looking ahead, we may see tiered digital duty credits and AI-driven stamping interfaces. Until then, combine proactive alerts with simple workflows to keep your practice on solid ground.
Frequently Asked Questions
Stamp duty often trips up even seasoned practitioners. Picture it like postage: the “package” (your document) has a “weight” (market value) and a “class” (instrument type), and the rate comes straight from the right tariff sheet.
To calculate duty on property transfers, follow three simple steps:
Step 1: Pin down the instrument and its market value.
Step 2: Find the matching entry in Schedule I–VIII.
Step 3: Multiply the rate by the consideration value and double-check your maths.
Draft Bot Pro feels like having a built-in calculator. It never lets you miss a revised rate or scope.
Insights
Draft Bot Pro’s Q&A assistant provides context-aware duty calculations and exemption guidance.
In-editor pop-ups deliver instant insights on rate changes and section references.
Customizable reminder tools ensure no FAQ (like Section 47 refunds) goes unnoticed.
Exemptions are another common question. Transfers between relatives, low-value agreements and government papers often qualify. And if a sale falls through, Section 47 offers a way back.
Insight: Under Section 47(c)(5), you can recoup 100% of the duty on a failed transaction—in just weeks, not months.
E-Stamp And Automation
E-stamp platforms make the process instant. You pay online, grab a secure code and embed it in your PDF. With Draft Bot Pro linked to leading gateways, codes are auto-generated and tracked for audit trails.
Automated alerts flag rate changes. Reminder nudges keep your review calendar on point. Custom reports show every pending stamp duty filing, slashing manual checks by over 70% while keeping you fully compliant.
Can I Integrate The Bombay Stamp Act Checks Into Existing Workflows?
Absolutely. Draft Bot Pro’s API slots into your document systems. Duty calculations, alerts and validation pop up right in your usual editor—no switching apps.
Key Takeaways
Quote the correct schedule entry in each draft for full transparency.
Always verify e-stamp codes in Draft Bot Pro to avoid last-minute rejections.
Set up alerts to catch amendments before they go live.
Keep exemption clauses on hand for swift refund applications.
Boost your efficiency with AI-powered stamp duty checks.
Start using Draft Bot Pro today for precise, up-to-date guidance on the Bombay Stamp Act.
Explore features and sign up at Draft Bot Pro