A Guide to India's Advocate Fee Rules
- Rare Labs
- Oct 21, 2025
- 17 min read
When you first look into hiring a lawyer in India, one of the biggest questions is always about the cost. Unlike buying something off a shelf, advocate fees aren't standardised. They operate in a market-driven system, which really just means the fee is a private deal between you and your advocate.
This results in a massive range of costs. There’s no single, fixed price list for legal services, and what you pay will swing wildly based on the lawyer's experience, how tricky your case is, and even the city you're in.
How Advocate Fees Actually Work in India
Let's be honest, staring at a legal bill can be a confusing experience. This is mainly because India doesn't have a uniform fee structure for advocates. Think of it less like a product with a price tag and more like a tailored service.
Understanding the common ways lawyers charge is the first step to getting some clarity and, more importantly, avoiding any nasty financial surprises down the road. These fee models are designed to fit different kinds of legal work and client needs, much like choosing a mobile plan—some people need a simple pay-as-you-go option, while others require an all-inclusive monthly package for heavy use.
This diagram breaks down the three most common fee models you'll encounter.
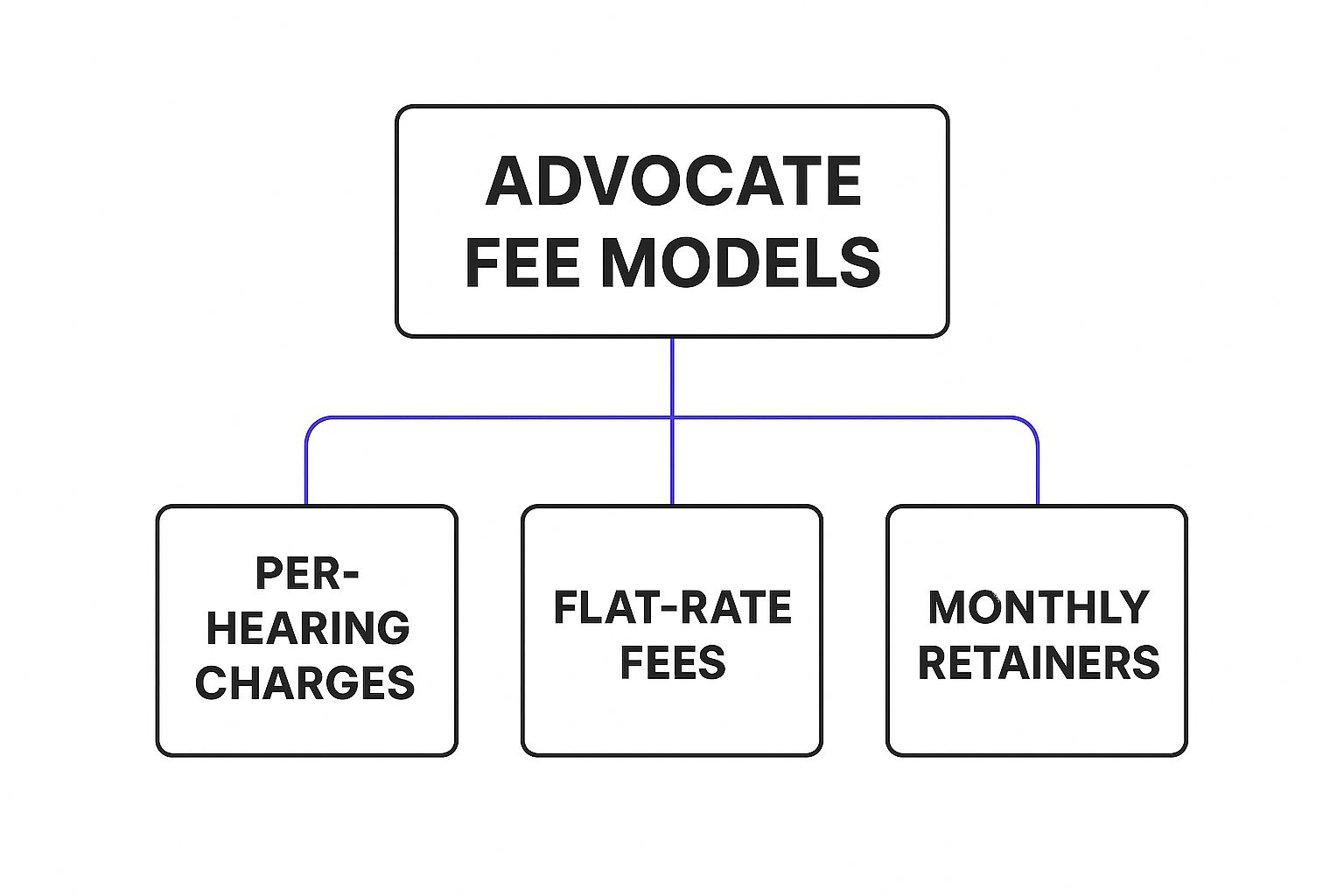
As you can see, the structure usually boils down to per-hearing charges, a flat fee, or a monthly retainer. Each one makes sense for different legal situations.
Common Fee Structures Explained
To give you a better idea of what to expect, let's take a closer look at the most prevalent fee models used by advocates across India. This table breaks down how each one works and when it might be the right choice for your situation.
| Common Advocate Fee Models at a Glance || :--- | :--- | :--- || Fee Model | How It Works | Best Suited For || Per-Hearing Charges | You pay the advocate a set fee for every single court appearance they make on your behalf. It’s a classic pay-as-you-go model. | Litigation matters, criminal cases, and any situation involving frequent court dates. || Flat-Rate Fees (Lumpsum) | A single, all-inclusive fee is agreed upon upfront for the entire case or a specific task, like drafting a will or a contract. | Straightforward legal tasks with a clear beginning and end, such as property registration, contract drafting, or uncontested divorces. || Monthly Retainers | You pay a fixed amount each month to have an advocate on call for ongoing legal advice and services as needed. | Businesses, startups, and individuals who require continuous legal support and consultation. |
Knowing which model is being used is crucial for managing your legal budget and ensuring there are no misunderstandings about what you're paying for.
The huge difference in fees also comes from the hierarchy within the legal world itself. A top senior advocate at the Supreme Court might charge anywhere from ₹5 lakh to ₹30 lakh for a single appearance. On the other hand, most lawyers earn far less. An Advocate-on-Record (AOR) in the Supreme Court, for instance, might charge between ₹6,000 and ₹10,000 per hearing.
InsightsGetting a handle on these models is your best defence against surprise costs. Make sure your fee agreement is crystal clear about the model, what work is covered, and any potential extra charges. A little bit of clarity upfront can prevent a lot of headaches later.
How Draft Bot Pro Can Help
Figuring out these fee agreements can feel overwhelming. A tool like Draft Bot Pro can be a massive help here. It can analyse your fee agreements, flag any vague or confusing terms, and even benchmark them against industry standards to ensure you're getting a fair deal.
It helps you and your advocate create a transparent agreement from the start, which is a fundamental part of protecting everyone's interests. This is something we cover in more detail in our guide to the rights of advocates in India. For law firms looking to manage client billing and finances efficiently, specialised software is often a game-changer. Services like Smart Advocate hosting solutions offer tools that can make this process a whole lot smoother.
The Laws That Govern What Lawyers Can Charge
You might think that when it comes to lawyers' fees in India, it's a bit of a free-for-all, driven purely by the market. But that's not quite the full picture. It’s better to think of it like a highway with wide lanes, but also very firm guardrails. These guardrails are put in place by specific laws and professional conduct rules, all designed to protect clients and uphold the integrity of the legal profession.
The cornerstone of this entire framework is the Advocates Act of 1961. This is the foundational law that established the Bar Council of India (BCI) and gave it the power to set the standards for how advocates must conduct themselves. In simple terms, the Act is the constitution for lawyers, and the BCI is the regulatory body that writes the actual rulebook.

This rulebook isn't just a collection of suggestions; it contains strict, mandatory guidelines that directly shape how lawyers can structure their fees. For any client, getting a handle on these core principles is non-negotiable.
Core BCI Prohibitions on Fees
The BCI has drawn some very clear lines in the sand about certain fee arrangements, mainly to stop legal services from being treated like any other commercial product. These aren't just best practices; they are hard and fast ethical obligations.
Two of the biggest no-gos are:
Ban on Contingency Fees: An advocate is absolutely forbidden from charging a 'contingency fee', sometimes called a 'success fee'. This means they can't take a percentage of whatever money is recovered in a lawsuit. The BCI's reasoning is sound: it could create a massive conflict of interest, tempting the advocate to chase a big payout rather than focusing on the client's actual best interests.
Prohibition on Advertising: You won't see lawyers advertising their services or openly soliciting work in India. This rule is there to reinforce the idea that law is a noble profession, not just another business, and it helps prevent misleading claims about success rates or cut-price fees.
These rules ensure that the relationship you have with your lawyer is built on fiduciary duty and trust, not just a simple business transaction.
Understanding Awarded Costs vs. Actual Fees
Here’s something that trips up a lot of clients: the idea of 'awarding costs' in a lawsuit. When a court sides with you, it might order the losing party to pay your 'costs'. This is where a crucial distinction comes in.
The amount the court awards as 'costs' is a nominal, almost symbolic sum calculated from a fixed court schedule. It is almost always a tiny fraction of what you have actually paid your lawyer.
InsightsIt's vital to understand that the 'costs' awarded by a court will not cover your total legal bill. Your fee agreement with your advocate is a completely separate contract, and you are on the hook for the full amount you agreed to, no matter what the court awards.
How Draft Bot Pro Can Help
Trying to make sense of these legal frameworks and BCI rules can feel overwhelming. This is where a sophisticated legal AI like Draft Bot Pro becomes an invaluable ally. When you're putting together a fee agreement, the tool can ensure the language is fully compliant with the Advocates Act and all BCI regulations.
For example, it can help you structure clauses that clearly spell out the scope of work and payment terms without accidentally straying into the territory of contingency fees. By generating compliant and transparent agreements, Draft Bot Pro helps both lawyers and clients start their professional relationship on a solid, ethical footing, which is the best way to minimise the risk of disputes over fees down the line.
Navigating High Court Fee Schedules and Rules
It’s a common point of confusion for clients: discovering that each High Court in India has its own official fee schedule. This often leads to a major misunderstanding about how advocate fees actually work. Many people jump to the conclusion that these schedules are a price list dictating what a lawyer is allowed to charge.
That’s not the case at all.
These schedules exist for a very specific, and often misunderstood, purpose that only comes into play after a lawsuit has concluded. They aren't a menu of legal service prices. Think of them as an internal tool the court uses for a process called the taxation of costs. This is simply the formal method for calculating the nominal amount the losing side has to pay the winning side.
Let's use an analogy. Imagine you take your car for a complex engine repair. The final bill will cover the mechanic's labour, diagnostic time, and overall expertise. The court's fee schedule is like a standardised price list for a few basic nuts and bolts used in the repair; it doesn't even begin to cover the mechanic's skill, the hours they put in, or the difficulty of the job. It's just a reference point for one small component of the total cost.
The True Purpose of Court Fee Schedules
At their core, these schedules are designed to bring a little predictability and fairness to how costs are awarded at the end of a case. When the dust settles, the court registrar pulls out this pre-approved list to calculate a standardised, symbolic amount. The goal is simply to partially offset the winner's litigation expenses, not to cover their entire legal bill.
It's absolutely critical to understand that these schedules have zero bearing on the private fee agreement you have with your advocate. Your contract with your lawyer is a completely separate, binding agreement. It reflects their expertise, the complexity of your case, and the sheer amount of work involved. The court's schedule, on the other hand, is just an administrative tool for post-judgment calculations.
InsightsWhile these official schedules don't limit what your advocate can charge, they are still a powerful tool. They offer a valuable benchmark for what the court itself considers a 'reasonable' fee for certain tasks. This can give you some useful context—and maybe even a little leverage—when you're negotiating your own fee agreement.
This distinction is fundamental. The fee you agree to pay your lawyer is a product of market realities and your mutual agreement. The 'costs' awarded by a court are based on a procedural rulebook. The two figures will almost never be the same.
Court Schedules vs Private Agreements
To really drive this point home, let's look at the two side-by-side. Getting your head around the different roles they play is essential for managing your legal budget and your expectations.
It’s easy to see why pointing to a court fee schedule to argue about your advocate's bill just doesn't work. They are built for entirely different functions within our legal system.
How Draft Bot Pro Can Help
Getting these details right, especially when drafting documents that touch on cost calculations, can be a real headache. This is where a legal AI assistant like [Draft Bot Pro](https://www.draftbotpro.com/) gives you a serious edge. You can feed the platform specific High Court rules and their fee schedules as reference material.
So, when you're preparing a bill of costs or any court document that refers to potential awarded fees, Draft Bot Pro ensures your figures are spot-on and perfectly aligned with that court's specific rules. This isn't just a time-saver; it adds a layer of precision that makes your submissions bulletproof. It ensures every cost-related claim is justified and fully compliant with advocate fee rules, preventing them from being shot down on a technicality.
Why 'No Win, No Fee' Agreements Are Banned
The idea of a 'no win, no fee' arrangement sounds incredibly appealing on the surface. You only pay if you win—what could be fairer, right? Yet, in India, this model, more formally known as a contingency fee, is strictly forbidden under the established advocate fee rules. This isn't just some arbitrary decision; it's a rule deeply rooted in the ethical foundations of the legal profession.
At its core, the ban is about preserving the integrity of the advocate-client relationship. The Bar Council of India (BCI) has always maintained that law is a noble profession, not just another business. A contingency fee arrangement, where a lawyer gets a percentage of the lawsuit's winnings, completely changes that dynamic. It essentially turns the relationship into a commercial venture.
Suddenly, the advocate becomes a financial stakeholder in the outcome of the case, which can create some serious ethical problems.

This structure is seen as a direct path to a conflict of interest. Think about it: an advocate's primary duty is to their client's best interests. But if their own payday is tied directly to the settlement amount, they might be tempted to push for a larger, riskier payout over a more sensible, secure settlement that truly benefits the client.
Upholding Professional Integrity
The Supreme Court of India has consistently backed this ban, reinforcing that the legal profession must maintain its service-oriented character. Time and again, the courts have ruled that such agreements are against public policy. The argument is that allowing advocates to have a financial stake in litigation could degrade the profession and chip away at public trust in the entire justice system.
The core principle is simple: an advocate's judgment must remain unbiased and focused solely on the legal merits of the case. Introducing a personal financial incentive threatens that crucial impartiality. This is a key part of the conduct rules that every advocate must follow, a topic we explore in more detail while navigating India's Conduct, Discipline, and Appeal Rules.
The Ongoing Debate
Despite the clear prohibition, this topic is still hotly debated. Proponents argue that banning contingency fees actually creates a barrier to justice. Their point is that people with legitimate cases but limited funds are often unable to afford legal representation, effectively shutting them out of the courthouse. In their view, 'no win, no fee' could be a powerful tool for access to justice.
On the flip side, opponents fear it would open the floodgates to frivolous lawsuits. If lawyers can take on cases with no upfront cost, they might be encouraged to file speculative claims, hoping for a quick settlement. This could clog the already overburdened court system and foster a more litigious culture.
InsightsThe ban on contingency fees highlights a fundamental tension in our legal system: the need to uphold professional ethics versus the goal of ensuring everyone has access to justice. While the current rules prioritise ethical integrity, the debate forces us to constantly ask whether the system adequately serves those without deep pockets.
How Draft Bot Pro Can Help
Ensuring a fee agreement is ethically sound and compliant with BCI rules is absolutely non-negotiable. This is where a tool like Draft Bot Pro becomes essential. When you're drafting fee structures, it can help you create clear, transparent agreements that properly define the scope of work and payment terms—all without ever crossing into the forbidden territory of contingency fees. The AI can even analyse your clauses to flag any language that might be misinterpreted as performance-based, making sure your agreements are always compliant with advocate fee rules and professional standards.
What to Do When You Are Charged Unfair Fees
That sinking feeling when you get a bill from your advocate that seems way out of line is deeply frustrating. It’s a stressful situation, but it's critical to know you're not powerless here. Indian law provides clear pathways for recourse when a fee feels unreasonable or unjust.
Just because there isn't a fixed government price list doesn't mean it's a free-for-all.
Your first, and strongest, line of defence is always a clear, written fee agreement. Think of this document as the foundation of your professional relationship. It should go beyond just the final number, detailing the exact scope of work, the fee structure, a payment schedule, and any potential extra costs. A solid agreement nips misunderstandings in the bud.
Taking Action Against Unreasonable Fees
So, what happens if a dispute blows up anyway? Whether you have an agreement or not, there are formal channels you can go through. The key is to be methodical and document absolutely everything. You are never expected to just accept a bill that feels completely disproportionate to the work done.
The most direct route is filing a complaint for professional misconduct with the relevant State Bar Council. This is a serious step, as significant overcharging is often viewed as a breach of professional ethics. The Bar Council has the power to investigate and can take disciplinary action against the advocate if they agree the fee was excessive.
The Complaint Process Explained
Filing a complaint is a structured process designed to be accessible. While the nuts and bolts might differ slightly from state to state, the general steps are pretty standard:
Draft a Formal Complaint: Write down your grievance clearly. Detail exactly why you believe the fee is unfair, including all relevant facts, dates, and the specific amount you're disputing.
Attach Supporting Documents: This part is vital. Gather copies of the fee agreement (if you have one), all receipts for payments, any relevant emails or letters, and any other scrap of evidence that backs up your claim.
Submit to the State Bar Council: File the complaint with the Bar Council where the advocate is registered. This kicks off their internal review process.
Beyond the Bar Council, you could also file a civil suit in court to recover the excess amount you paid. This path is generally more time-consuming and comes with its own legal costs, but for significant sums, it can be an effective option. It might also be worth looking into our guide to Section 12 of the Consumer Protection Act, as it can sometimes apply to disputes over professional services.
InsightsThe most critical takeaway is that the principle of 'reasonableness' always applies. An advocate doesn't get a blank cheque just because there's no official fee schedule. Your right to a fair fee is protected by the ethical standards of the legal profession, and there are established bodies to enforce them.
How Draft Bot Pro Can Help
As with most problems, prevention is the best cure. This is where a tool like Draft Bot Pro becomes incredibly useful. Instead of relying on a handshake or a flimsy template, you can use the platform to generate a comprehensive and crystal-clear fee agreement right from the start.
By defining the precise scope of work, outlining payment milestones, and clarifying what counts as an extra expense, Draft Bot Pro helps create a document that protects both you and your advocate. It eliminates the ambiguity that causes most fee-related conflicts in the first place. Kicking off a professional relationship with this level of clarity is the single best way to keep disputes from ever happening.
The Real Impact of Fee Disparity on Justice
The rules around advocate fees aren’t just dry regulations on a page; they have a massive, real-world impact on justice for everyday people. India’s market-driven system has, over time, created a troubling chasm between the elite legal firepower the wealthy can afford and the representation an ordinary citizen can access. This financial gap can turn the courtroom into an uneven playing field.
Too often, the outcome of a case is swayed more by financial muscle than the actual legal merit of the arguments. When one side brings in a top-tier senior advocate and the other struggles to keep up, the core principle of equal access to justice starts to wear thin. This is the critical socio-legal reality you have to understand before diving into the fee system itself.

This disparity isn't a minor flaw—it strikes right at the heart of fairness in our legal system. It proves that understanding advocate fee rules isn't just about money; it’s a fundamental part of figuring out how to navigate the justice system effectively.
The Two Tiers of the Legal System
Nothing shows this gap more clearly than the fees charged by the country's most famous senior advocates. Because India has historically let the market decide these fees, top legal minds like Ram Jethmalani, Fali Nariman, and Harish Salve have reportedly charged anywhere from ₹6 lakh to ₹30 lakh for a single appearance in a High Court or the Supreme Court.
For example, Ram Jethmalani’s fees were known to hit ₹25 lakh per appearance, while Harish Salve’s can go as high as ₹30 lakh per case. These are astronomical sums, completely out of reach for the vast majority of citizens, and they create a stark divide in who gets top-tier legal representation. You can dig deeper by exploring the research on the impact on the legal services market.
What this really means is that we have a two-tiered system of justice. There’s one tier for those who can afford the best legal brains in the country, and another one for everyone else.
The Limits of Legal Aid
Now, India does have a legal aid framework designed to bridge this very gap, but its resources are often stretched to the breaking point. Legal aid services, as crucial as they are, often grapple with overwhelming caseloads and tight budgets.
Let's be realistic: they can't compete with the resources and singular focus that a high-fee private advocate can pour into a complex case.
This reality means that for many people, even when they have a strong case, the thought of going up against an opponent with a seemingly bottomless legal budget is terrifying. It can push individuals and small businesses to accept unfair settlements or even abandon valid claims because they simply can't afford a long, drawn-out legal fight.
InsightsThe disparity in legal fees is more than just a number; it's a structural barrier to the promise of "justice for all." It shows just how urgently we need a more balanced system where legal merit, not financial power, truly decides the outcome of a case.
How Draft Bot Pro Can Help
While AI can’t fix systemic inequality overnight, it can help level the playing field in very practical ways. For younger advocates or smaller law firms representing clients with limited budgets, efficiency is everything. Draft Bot Pro helps them conduct high-quality legal research and create precise documents in a fraction of the time.
This boost in efficiency means they can manage their resources better, enabling them to take on tougher cases and provide strong representation without getting bogged down in administrative tasks. By automating the routine work, Draft Bot Pro frees up lawyers to focus their energy on strategy and advocacy—helping to close the resource gap and give their clients a much stronger fighting chance.
Got Questions About Advocate Fees? We’ve Got Answers.
When you're dealing with a legal issue, the last thing you want is confusion over your advocate's fees. Getting a handle on your rights and the standard way of doing things is the best way to feel confident. Let's tackle some of the most common questions with straightforward, practical answers.
Is a Written Fee Agreement an Absolute Must?
While there's no strict law that says you must have a separate, detailed fee agreement, moving forward without one is a big mistake.
Think of it this way: the Vakalatnama you sign is just the permission slip allowing your advocate to represent you. It's not a contract that spells out payment terms. A clear, written agreement is your best defence against misunderstandings over the scope of work, when payments are due, and what counts as an extra cost. It nips potential disputes in the bud.
Can My Lawyer Hold My Case Files Hostage for Payment?
Absolutely not. This is a huge no-no.
The Bar Council of India and countless court rulings have been crystal clear on this. An advocate has no legal right to keep your case papers or refuse to give you a No Objection Certificate (NOC) just because of unpaid fees. It's considered professional misconduct because it sabotages your case and gets in the way of your fundamental right to representation. Your files are your property.
What's the Real Difference Between "Fees" and "Costs"?
This is a classic point of confusion, and it's an important one to get right. The two terms sound similar but are worlds apart in a legal setting.
Advocate's Fee: This is the private deal you strike with your lawyer for their time, expertise, and professional services. It’s a contract based on their experience, how complex your case is, and the work you’ve both agreed on.
Court Costs: This is a much smaller, often symbolic, amount that a court might order the losing side to pay the winner. It's meant to slightly offset the expenses of going to court and is calculated from fixed schedules. It will almost never come close to covering your actual advocate's fee.
InsightsThe most critical thing to remember is that the "costs" awarded by a court will never cover your entire legal bill. Your fee agreement is a separate, binding contract that you are responsible for, no matter what the court's final order on costs says.
How Do I Know if a Fee Quote Is Fair?
Since there isn't an official government-set cap on fees, "reasonable" can feel a bit vague. But it's not a free-for-all. Any fee has to be justifiable based on the actual work involved.
To make sure you're getting a fair price, do a little homework. Look up what advocates typically charge for similar cases in your city. More importantly, ask for a detailed breakdown of what their quote includes. And never, ever hesitate to get a second opinion from another advocate. It's a standard, smart move that gives you proper perspective.
How Can Draft Bot Pro Help with This?
The best way to build trust and confidence is to make sure your fee agreements are rock-solid and leave no room for doubt. A legal AI tool like Draft Bot Pro can generate robust agreement templates that clearly define every part of the service, from the scope of work to payment milestones. This wipes out any ambiguity and prevents future arguments about advocate fee rules.
Ready to draft clear, compliant, and dispute-proof legal documents? Draft Bot Pro is the AI-powered legal assistant trusted by over 46,000 legal professionals in India to create precise documents and conduct verifiable research in minutes. Visit https://www.draftbotpro.com to see how it can improve your practice.